Relief Visualization Toolbox (RVT)
Project Team
Žiga Kokalj, PhD, assoc. prof. , Klemen Zakšek, PhD, Peter Pehani, Klemen Čotar, Maja Somrak, Nejc Čož, PhD-
Duration
2 September 2013 -
Project Leader
-
Financial Source
Slovenian Research Agency
European Commission's Culture programme
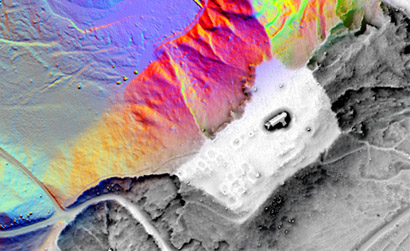
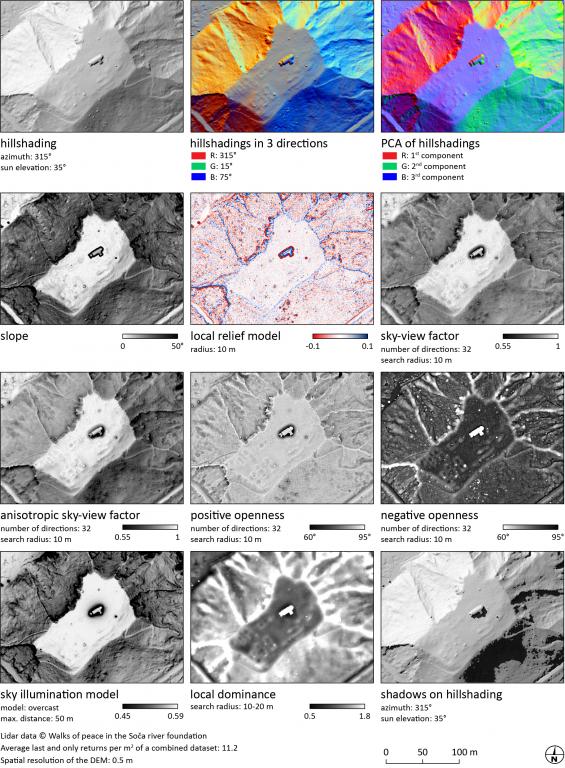
Relief Visualization Toolbox was developed to help scientist visualize raster elevation model datasets. We narrowed down the selection to include techniques that have proven to be effective for identification of small scale features. Default settings therefore assume working with high resolution digital elevation models, derived from airborne laser scanning missions (lidar).
Despite this, techniques are also used for different other purposes. Sky-view factor, for example, can be efficiently used in numerous studies where digital elevation model visualizations and automatic feature extraction techniques are indispensable, e.g. in geography, geomorphology, cartography, hydrology, glaciology, forestry and disaster management. It can be used even in engineering applications, such as, predicting the availability of the GPS signal in urban areas.
Methods currently implemented are:
- hillshading,
- hillshading from multiple directions,
- PCA of hillshading,
- slope gradient,
- simple local relief model,
- sky-view factor (as developed by our team),
- anisotropic sky-view factor,
- positive and negative openness,
- sky illumination, and
- local dominance.
For a more detailed description see references given at each method in the manual and a comparative paper describing them (e.g. Kokalj and Hesse 2017, see below).
RVT supports elevation raster file data conversion. It is possible to convert all frequently used single band raster formats into GeoTIFF, ASCII gridded XYZ, Erdas Imagine file and ENVI file formats. Mosaicking of multiple files, e.g. tiled lidar elevation models, works well if data are reasonable, i.e. if all the files have the same projection, resolution, square pixels etc.
Development of RVT was part financed by the European Commission's Culture Programme through the ArchaeoLandscapes Europe project and by the Slovenian Research Agency core funding No. P2-0406, and by research projects No. J6-7085 and No. J6-9395.
A bug: PCA does not work with large files.
Downloads
Relief Visualization Toolbox Standalone version (EXE), Windows 64-bit, version 2.2.1
Relief Visualization Toolbox manual, version 2.2.1 (Instructions for use).
Documentation for RVT in Python, QGIS and ArcGIS raster functions.
GitHub
RVT standalone (IDL)
RVT Python functions (rvt_py)
RVT ArcGIS raster functions
RVT QGIS plugin
Please report any bugs and suggestions for improvements.
References
When using the tools, please cite:
- Kokalj, Žiga, 2025. Standardizing visualization in ancient Maya lidar research: techniques, challenges and recommendations. Archaeological prospection.
- Zakšek, K., Oštir, K., Kokalj, Ž. 2011. Sky-View Factor as a Relief Visualization Technique. Remote Sensing 3(2): 398-415 .
Further reading
- Kokalj, Ž., Somrak, M. 2019. Why Not a Single Image? Combining Visualizations to Facilitate Fieldwork and On-Screen Mapping. Remote Sensing 11(7): 747.
- Kokalj, Žiga, Ralf Hesse. 2017. Airborne laser scanning raster data visualization: A Guide to Good Practice. Ljubljana: Založba ZRC.
Images
Note: click to enlarge, press ESC to quit.